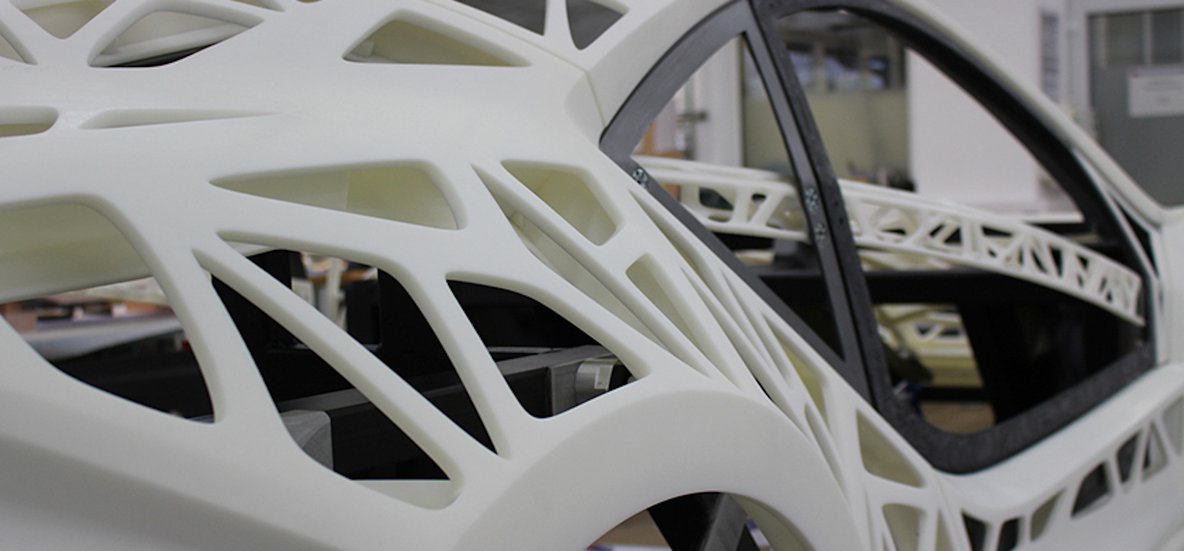
Once confined to prototyping, 3D printing has exploded onto the automotive scene, revolutionizing everything from design iterations to final production parts. A report revealed that the global 3D printing market in the automotive industry is projected to surpass $7.31 billion by 2034, a testament to its growing influence.
At its core, 3D printing—or additive manufacturing—builds objects layer by layer from digital models. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which cut away material to form a shape, 3D printing allows for unparalleled design freedom, customization, and efficiency. Its advantages include rapid prototyping, reduced waste, and the ability to create complex structures with precision.
3D printing is fundamentally altering the automotive landscape, impacting design, manufacturing, and even the overall consumer experience. From accelerated design iterations to on-demand manufacturing, this technology is driving the industry toward a more innovative and sustainable future.
Design & Prototyping
3D printing enables engineers to rapidly prototype complex shapes and geometries, significantly speeding up the design process. Traditional methods of creating prototypes often take weeks, but with 3D printing, designs can be brought to life in mere hours. This accelerated timeline allows for more frequent testing and refinements, fostering innovation. For instance, General Motors used this innovation to develop lightweight seat brackets, reducing production time and material costs while maintaining structural integrity.
- Improved Design Flexibility: The ability to create intricate internal structures and complex geometries is one of 3D printing’s standout features. Engineers can design components with lattice structures that are lighter yet stronger, enhancing vehicle performance and efficiency. An example is Bugatti’s use of 3D printing to produce titanium brake calipers with intricate designs that would be unachievable with traditional manufacturing methods. This flexibility paves the way for parts that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Personalized Design: Mass customization is another transformative aspect of 3D printing. Drivers can now have vehicles tailored to their unique preferences, from personalized interior panels to custom exterior trims. In the high-performance segment, automakers like Porsche are leveraging 3D printing to offer bespoke racing seats that perfectly contour to a driver’s body. This level of personalization not only enhances the driving experience but also raises questions about the ethical and societal implications of creating vehicles as unique as their owners.
Manufacturing & Production
Reduced Lead Times: By cutting down the time needed to manufacture components, 3D printing enhances production efficiency. This reduction in lead time minimizes inventory costs and shortens the supply chain. Automakers like BMW use 3D printing to produce customized fixtures and tools, significantly accelerating the assembly line’s pace and adaptability.
On-Demand Manufacturing
The concept of distributed manufacturing—producing parts locally using 3D printers—is gaining traction. This approach reduces reliance on global supply chains, leading to faster turnaround times and lower transportation costs. For example, Ford employs on-demand 3D printing to produce replacement parts for older vehicles, ensuring availability without maintaining extensive inventories.
Production of Complex Components
Traditionally, certain components were impossible or prohibitively expensive to produce due to their complexity. 3D printing changes this by allowing intricate designs to be manufactured with ease. Companies like Koenigsegg are using such mechanisms to create engine components with integrated features, enhancing performance while reducing weight. Similarly, entire vehicle subframes are being printed, showcasing the technology’s potential to revolutionize how cars are built.
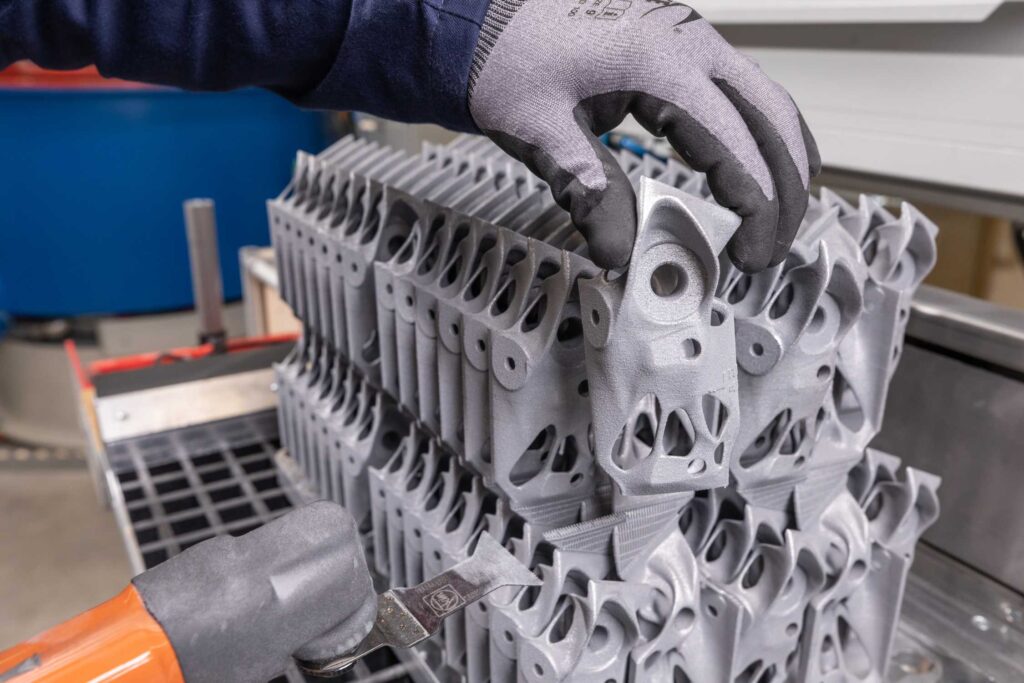

The Future of 3D Printing in Automotive
Emerging Technologies
Advancements in 3D printing technologies are poised to further reshape the automotive industry. Metal 3D printing, for example, enables the creation of high-strength components with remarkable precision, making it suitable for critical parts like engine blocks and structural elements. Meanwhile, 4D printing introduces materials that can self-assemble or adapt to environmental changes, offering futuristic possibilities for dynamic car components. Bioprinting, though still in its infancy, hints at a future where organic materials could be integrated into vehicle manufacturing, such as bio-composites for sustainable interiors.
- Sustainability Considerations: The environmental impact of 3D printing is a critical area of focus. While additive manufacturing generates less waste compared to traditional methods, the energy consumption of 3D printers remains a concern. However, innovations like using bio-based materials or recycled polymers in printing processes are making strides toward sustainability. For instance, some companies are experimenting with printing car parts from recycled plastic, reducing the ecological footprint of manufacturing.
- The Role of AI and Automation: Artificial intelligence and automation are increasingly being integrated into 3D printing workflows. AI-driven design tools can optimize part geometries for strength and material efficiency, while automated quality control systems ensure consistent output. Fully automated printing factories, where machines handle design, production, and finishing processes autonomously, are on the horizon. Such facilities could revolutionize mass production, making it faster, cheaper, and more scalable.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Despite its advantages, 3D printing in automotive manufacturing faces several limitations. Material constraints remain a significant hurdle, with many 3D printers limited to specific plastics or metals. Build size limitations restrict the production of larger components, while the high costs associated with 3D printing make it less viable for mass production. Overcoming these challenges requires continued investment in research and development to expand material options, improve scalability, and reduce costs.
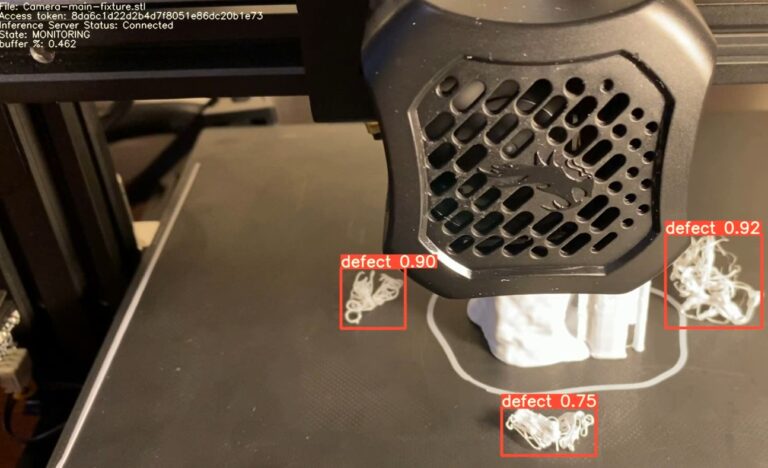
Ensuring the safety and reliability of 3D-printed automotive components is critical. Variations in printing quality can lead to structural weaknesses, making robust quality control measures essential. The development of industry standards and certification processes for 3D-printed parts is key to gaining widespread adoption. Automakers are increasingly adopting advanced inspection technologies, such as X-ray imaging and AI-driven defect detection, to ensure component integrity.

Conclusion
3D printing is transforming the automotive industry, driving innovation in design, manufacturing, and sustainability. From rapid prototyping to localized production, the technology is paving the way for a more efficient and customized automotive future.
As such printing technologies continue to evolve, their potential to revolutionize vehicle design, manufacturing, and consumer experience grows. The integration of emerging technologies, sustainable practices, and AI-driven automation will define the next chapter of automotive innovation. To fully embrace this transformation, industry professionals and enthusiasts alike should explore the limitless possibilities of these technologies.